LEAD SERVICE LINE REPLACEMENT
Lead Service Line Replacement and Notification Act (Public Act 102-0613)
The Lead Service Line Replacement and Notification Act (Public Act 102-0613) mandates that all public water suppliers in Illinois create a comprehensive water service line material inventory for all properties supplied with water in the community. To meet this mandate, the Village of Antioch needs your help collecting information on the material of the water service line in your house.
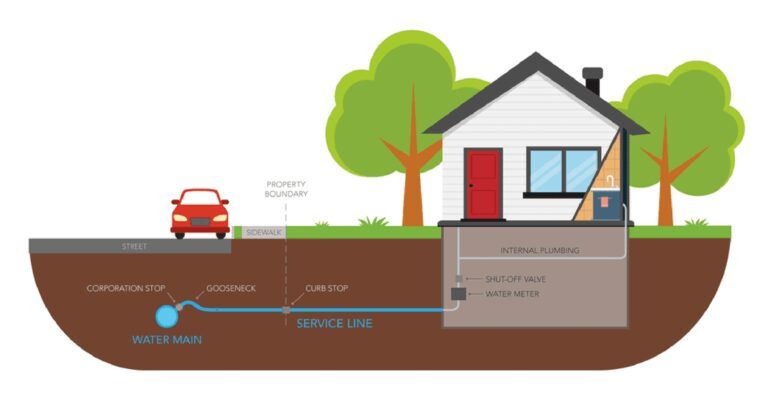
Water service lines are the pipes along your property that run from the City’s water main to the water meter inside your home (see diagram below). Common water service line materials found in homes include copper, lead, galvanized steel, and plastic. Congress banned the use of lead service line pipes in 1986 to protect public health. However, if your house was built before 1986, your water service line may be made from lead.
How to Identify Water Service Line Material
Tools needed:F lathead Screwdriver, Refrigerator Magnet, and a Penny
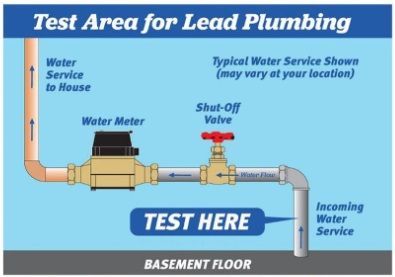
Step One: Locate the water service line coming into the building.
This is typically found in the basement. A valve and the water meter are installed on the pipe after the point of entry.
Identify a test area on the pipe between the point where it comes into the building and the valve. If the pipe is covered or wrapped, expose a small area of metal.
Step Two" Scratch the surface of the pipe.
Use the flat edge of the screwdriver to scratch through any corrosion that may have built up on the outside of the pipe.
DO NOT use a knife or other sharp instrument and take care not to puncture a hole in the pipe.
Step Three: Compare your findings to the chart below.
Each type of pipe will produce a different type of scratch, react to the magnet differently and produce a unique sound when tapped with a metal coin.
Lead Pipe
The Scratch Test
If the scraped area is shiny and silver, your service line is lead.
The Magnet Test
A magnet will not stick to a lead pipe.
The Tapping Test
Tapping a lead pipe with a coin will produce a dull noise.
Galvanized Pipe
The Scratch Test
If the scraped area remains a dull grey, your service line is galvanized steel.
The Magnet Test
A magnet will stick to a galvanized pipe.
The Tapping Test
Tapping a galvanized pipe with a coin will produce a metallic ringing noise.
Copper Pipes
The Scratch Test
If the scraped area is copper in color, like a penny, your service line is copper.
The Magnet Test
A magnet will not stick to a copper pipe.
The Tapping Test
Tapping a copper pipe with a coin will produce a metallic ringing noise.